Conservation giants implicated in public health crises among "Pygmies"
January 8, 2018
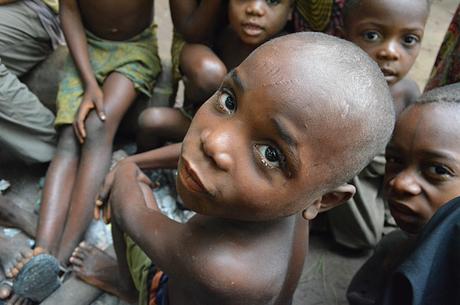 © C. Fornellino Romero/Survival
© C. Fornellino Romero/SurvivalThis page was last updated in 2017 and may contain language which is now outdated.
A Congolese organization has recently raised concerns that conservation contributed to the deaths of several dozen children, mostly Bayaka “Pygmies,” during an epidemic in 2016 in the Republic of Congo – the latest in a long line of related reports.
The deaths have been attributed by a medical expert to malaria, pneumonia and dysentery, aggravated by severe malnutrition.
Conservation-related malnutrition among Bayaka children in this region has been reported since 2005 at least, as the Bayaka are prevented from hunting and gathering on their lands by wildlife guards through violence and intimidation.
These guards are funded and equipped by the Wildlife Conservation Society (WCS), one of the world’s largest conservation organizations, and the logging company it has partnered with, CIB. Both organizations have failed to take effective action to prevent abuse.
“The wildlife guards abuse us. They don’t want us to go into the forest. How can we feed our children?” a Bayaka man from Mbandza, the site of the epidemic, told Survival in 2016.
These guards have been accused of abusing Bayaka and stealing their food for over 13 years. One such attack that took place in Mbandza in early 2016 left one man hospitalized.

In this way, the Bayaka are being illegally evicted from their ancestral homelands by threat of violence. As one Bayaka woman explained: “If we go into the forest we eat well there compared to the village. We eat wild yams and honey. We want to go into the forest but they forbid us to. It frightens us. It frightens us.”
Critics have noted that the guards have also failed to protect the wildlife the Bayaka depend on for food, since they have difficulty tackling corruption and the creation of logging roads, the two main drivers of poaching.
Plummeting health has been reported among Bayaka living in the Dzanga-Sangha Protected Areas in the Central African Republic – one of the World Wildlife Fund’s (WWF) flagship projects – since 2006. Conditions encountered among older women “would be considered a public health crisis by international health agencies," according to research published in 2016.
Increased malnutrition and mortality have been reported among Baka “Pygmies” in Cameroon, where WWF also operates, and among Batwa “Pygmies” in another of WCS’s project sites in east Democratic Republic of Congo.
“Now we are afraid of the anti-poaching squads. Before when a woman gave birth we took her to the forest to help her regain her strength and weight, now we can’t do this. We would take our children to the forest to avoid epidemics. Now we know illnesses we never knew before,” one Baka woman in Cameroon told Survival.
Watch Baka describe the abuse they face as a result of WWF’s conservation projects
Liquid error: internal
Neither WCS nor WWF has attempted to secure the Indigenous peoples’ consent, as basic due diligence and their own human rights policies require.
Survival’s Director Stephen Corry said: “Land theft is a serious and deadly crime, as these reports show. Many associate conservation with reason and compassion but, for Baka and Bayaka, it often means mindless violence and plummeting health. When will WWF and WCS finally start complying with their own human rights policies? ”
Timeline
1996: The organization Berggorilla & Regenwald Direkthilfe finds that malnutrition and mortality has increased among Batwa “Pygmies” since they were evicted from Kahuzi-Biega, a national park in east Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) funded by WCS.
1997: WWF observes that the fact that the Bayaka are banned from hunting or gathering inside the Dzanga-Ndoki Park, the park in the Central African Republic (CAR) that WWF helped to create, “punishes [the Bayaka] severely” and is undermining their food security.
2000: A study finds that the Batwa in Kahuzi-Biega, DRC, are suffering from nutritional deficiencies, because they are no longer able to hunt in the forest, and soaring mortality rates. Malnutrition is particularly pronounced among women and children.
2004: A BBC investigation into CIB’s logging concessions in Congo hears from a Bayaka man: “We get so much suffering because of [wildlife] guards. We can’t go and find things in the forest as we used to. All we hear is hunger.”
2004: Bayaka from another community in Congo report to Greenpeace: “Then we met another white man (WCS) who came to tell us to stop hunting and that the wildlife guards would make sure we did. Now we are afraid to go far in the forest in case the wildlife guards catch us so we have to stay in the village. […] Now we are dying of hunger.”
2005: The Congolese Observatory on Human Rights, the organization that reported on the 2016 epidemic, documents three cases of violent abuse against Bayaka by wildlife guards, and warns that some Bayaka “are dying of hunger.”
2005: A news report recounts how Bayaka in one of CIB’s logging concessions describe being targeted by wildlife guards that mistreat and temporarily imprison them, and how this has led to more frequent malnutrition among children and vulnerable adults.
2006: WWF and its partners commission a report that finds that the Bayaka in Dzanga-Sangha, CAR, are struggling to feed themselves. The Bayaka interviewed for the report state that the conservation project has forced them out of some of their richest hunting and gathering grounds. They report that wildlife guards harass or attack them even when they try to use the reduced areas of land they have left, all the while accepting bribes from the real poachers who were emptying the forest of its wildlife. Some Bayaka women are finding it so hard to find food, the investigator hears, that they have been driven to sex work in the nearby town.
2006: An article in The Lancet cautions that “Pygmy peoples’ health risks are changing as the central African forests, which are the basis for their traditional social structure, culture, and hunter-gatherer economy, are being destroyed or expropriated by […] conservation projects:”
2008: UNICEF warns that the Bayaka’s right to gather resources is being “flouted on the most basic level because Indigenous people no longer have access to areas rich in game” due to protected areas in Congo.
2012: An anthropologist with 18 years’ experience working with Bayaka in Congo reports increasingly poor nutrition and increased mortality. He attributes this to the removal of forest resources by loggers and to “conservationists’ exclusionary and draconian management practices.”
2013: A researcher at the University of Oxford reports that the combined impact of conservation and logging have led to poorer health and higher levels of drug and alcohol addiction among the Bayaka. He argues that conservation efforts would benefit from gaining people’s consent
2014: A medical study finds that “punitive anti-poaching measures” and dwindling wildlife have caused health to plummet among Bayaka in Dzanga-Sangha, CAR, particularly among women. “It is disheartening to see health decline so closely tied […] to the conservation management policies of the last twenty-five years,” the study’s authors note.
2015: A doctor with extensive experience working in CIB’s logging concessions reports that: “Aside from wounds inflicted by gorillas, buffalo or other wild animals, my colleague and I also see [gun] wounds in people claiming to have been attacked – sometimes without warning – by the protectors of wildlife: the wildlife guards.”
2015: The same doctor tells Survival: “I find this [wildlife guard violence] a very serious problem and in my opinion most wildlife guards have other motives than protecting the animals to work as a wildlife guard.”
2016: A second doctor with extensive experience working in CIB’s logging concessions describes to Survival the seasonal malnutrition she encounters among Bayaka, which she attributes to repressive conservation policies.
“Pygmy” is an umbrella term commonly used to refer to the hunter-gatherer peoples of the Congo Basin and elsewhere in Central Africa. The word is considered pejorative and avoided by some tribespeople, but used by others as a convenient and easily recognized way of describing themselves.




